Musculoskeletal Conditions
What are Musculoskeletal Conditions?
Musculoskeletal conditions affect the bones, muscles, and joints. Long-term (chronic) musculoskeletal conditions affect 3 in 10 Australians. Common chronic musculoskeletal conditions include:
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Osteoporosis
Back pain and problems, such as scoliosis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. It is a long-term condition where the joints in your body become inflamed and damaged. The cartilage layer that protects the ends of your bones begin to wear away causing the joint space to narrow. Osteoarthritis can cause pain, stiffness and restrict movement. The condition often affects knees, hips, and the spine. While this can worsen over time, osteoarthritis can be managed effectively with regular exercise, healthy eating, and special devices (footwear, braces, and orthoses).
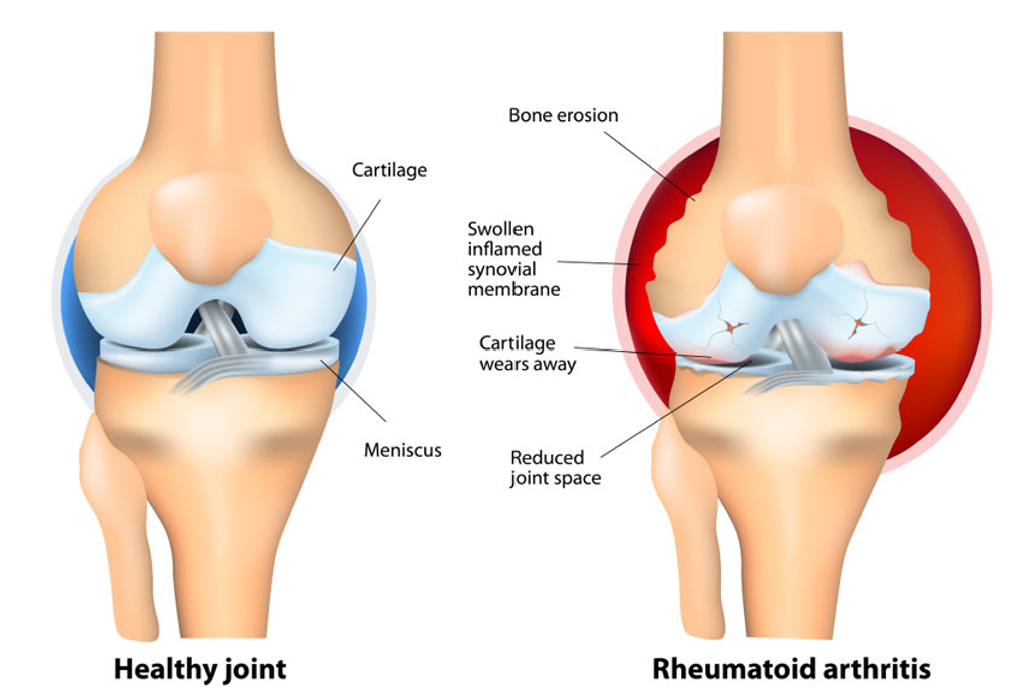
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease where your immune system does not recognize the tissue lining in your joints to be a part of your body and attacks it. When this happens, joints become swollen and painful. Rheumatoid arthritis usually affects smaller joints, such as those in your hands and feet, but can also affect larger joints like your knees and hips. People with this condition often experience ‘flare ups’ where your joints become particularly sore. There is no cure for Rheumatoid arthritis, but a combination of medical treatments and exercise therapy can manage your symptoms and slow down the progression.
Osteoporosis
As natural response, bones become weaker as we get older. However, this process can occur sooner and more quickly in people who have osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a reduction of bone density resulting in fragile bones. This can increase the risk of bone fractures (break) when a mild injury or minor fall occurs. Osteoporosis can be managed with exercise and medication to strengthen your bones, and through lifestyle changes to decrease your risk of falls.
Back Pain and conditions
Back pain is a very common problem: 1 in 6 Australians report having back problems. People experience back pain in different ways. Some experience a sharp pain, others report a dull ache or spasms. You may feel stiff or find it hard to turn or bend in certain directions. The cause for back pain is different for each individual. The spine is a complex interplay of different structures including vertebraes, discs, joints, ligaments, and muscles. Majority of the time, the pain is not a result of significant damage to the spine and is often due to the surrounding muscles, ligaments or joints. For at least 9 in 10 people, back pain is not caused by any particular injury or condition and is commonly referred as non-specific back pain. This type of back pain may be due to a range of different factors such as:
Postural changes
Muscle weakness
Muscle strain or spasm
Stationary positions (being in a certain position for a long period of time i.e. sitting or standing)
Living a sedentary life (not participating in enough physical activity throughout the day)
Overweight
Back pain can be prevented by lifestyle changes. Regular exercise to keep your spine flexible and strong, as well as building muscle strength to help support the spine. Maintaining good posture and a healthy weight is also vital.
How we can help:
We have a team of qualified Physiotherapists and Occupational Therapists that can provide further education and insight about the management of your condition and offer pain management strategies.
Physiotherapy can develop an individualised exercise program to meets your needs, whether that is to improve strength and mobility of your muscles and joints, or to improve your balance and reduce risk of injuries and falls.
Our team of Occupational therapists can help with managing those lifestyle changes and help implement a plan to help you get started.
Our physiotherapists and occupational therapists can help prescribe certain aids to assist in your daily life.
Our team of clinicians will help you come up with a plan so you can take charge of your own help and self-manage.